ratiTHE AMERICAS, WEST AFRICA, AND EUROPE – SECTION 1
- Ancient Cultures arrived about 22,000 years ago via a land bridge
- Earliest settlers were hunters
- Agriculture thrived starting about 5,000 years ago
- Some Natives remained Nomadic
- Maya, Aztec, and Inca societies flourished
national geographic
The first use of the name "America" was in 1507, when a new world map was created based on the explorations of Amerigo Vespucci.
EARLY BRITISH COLONIES – SECTION 3
Known among his peers as "an ardent smoker," John Rolfe introduced the tobacco plant to the Virginia colony. This plant became the cornerstone of the Virginia economy.
Tobacco cultivation was demanding work. Signs such as this one were posted in England to round up more workers (indentured servants).
New England Colonists (Puritans) soon conflict with the Native Americans over land & religion
King Philip’s War was fought in 1675 between the Natives and Puritans ending a year later with many dead and the Natives retreating
Portrait of Young William Penn in Armor, date and artist unknown.
Throughout the 1600s and 1700s, more British Colonies were established
By 1752, the English Crown had assumed more & more responsibility for the 13 colonies
Mercantilism & Navigation Acts were two such ways that the English government controlled the colonies
NAVIGATION ACTS
1651- England’s Parliament passed a series of laws known as the Navigation Acts
These laws restricted the colonies shipping & trade
Ships, destinations, crews, goods: All strictly regulated by the English
The colonies were developing a spirit of self-determination. Therefore, they were NOT happy with these restrictions
AFRICANS MAINTAIN PARTS OF THEIR CULTURE
Despite enslavement, Africans coped with the horrors of slavery via music, dance, and storytelling
Slaves also resisted their position of subservience by faking illness, breaking tools, or work slowdowns
Others were more radical and tried escape & revolt
Captain George Washington in the French and Indian War.
Painting by Junius Brutus Stearns, circa 1850. Courtesy Virginia Museum of Fine Arts.
Washington eventually defeated the French
Treaty of Paris ends the war in 1763
Brits claim most of North America including Florida (from French ally Spain) & Canada
Native Americans also realized a French loss was a Native American loss
PROCLAMATION LINE OF 1763
e population
- Ancient Cultures arrived about 22,000 years ago via a land bridge
Silk Road
The Silk Road is neither an actual road nor a single route. The term instead refers to a network of routes used by traders for more than 1,500 years, from when the Han dynasty of China opened trade in 130 B.C.E. until 1453 C.E., when the Ottoman Empire closed off trade with the West.
- Earliest settlers were hunters
- Agriculture thrived starting about 5,000 years ago
- Some Natives remained Nomadic
- Maya, Aztec, and Inca societies flourished
national geographic
Cosmology
 | |||
| Page 51 of Book IX from the Florentine Codex. The text is in Nahuatl; World Digital Library. |
General History of the Things of New Spain by Fray Bernardino de Sahagún: The Florentine Codex
Description
In partnership with Nahua men who were formerly his students at the Colegio de Santa Cruz de Tlatelolco, Sahagún conducted research, organized evidence, wrote and edited his findings starting in 1545 up until his death in 1590. The work consists of 2,400 pages organized into twelve books; more than 2,000 illustrations drawn by native artists provide vivid images of this era. It documents the culture, religious cosmology (worldview) and ritual practices, society, economics, and natural history of the Aztec people. One scholar described The Florentine Codex as “one of the most remarkable accounts of a non-Western culture ever composed.”
NATIVE AMERICAS IN 1400's
Native American societies in North America were as varied as the geography
The Pueblo (SW)
 |
| Taos Pueblo |
 |
Legacy and honors |
On September 22, 2005, the statue of Po'pay, (Popé) the leader of the Pueblo Revolt, was unveiled in the Capitol Rotunda in Washington, D.C. The statue was the second commissioned by the state of New Mexico for National Statuary Hall; it was the 100th and last to be added to the collection, which represents the Senate. It was created by Cliff Fragua, a Puebloan from Jemez Pueblo, New Mexico. It is the only statue in the collection created by a Native American.
Taos Pueblo village, where Po'Pay went into hiding to plan the revolt against the Spanish.
Getty Images
The Iroquois (/ˈɪrəkwɔɪ/ or /ˈɪrəkwɑː/), also known as the Haudenosaunee /ˈhoʊdənɵˈʃoʊni/, are a historically powerful and important northeast Native American confederacy. They were known during the colonial years to theFrench as the "Iroquois League" and later as the "Iroquois Confederacy", and to the English as the "Five Nations" (before 1722) and later as the "Six Nations", comprising the Mohawk, Onondaga, Oneida, Cayuga, Seneca, andTuscarora nations.
 |
| The four "Mohawk Kings" who travelled to London in 1710. |
 |
| Engraving based on a drawing by Champlain of his 1609 voyage. It depicts a battle between Iroquois and Algonquian tribes near Lake Champlain and Iroquois (NE) were two famous tribes |
Most of the tribes in America had common religious views, trade patterns & values
WEST AFRICAN SOCIETIES OF THE 1400S
 |
The Empire of Songhai Image Courtesy of The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History, Image © The Metropolitan Museum of Art |
 |
| Benin city in the 17th century. |
Long established, sophisticated societies existed in Western Africa
The Kingdom of Songhai controlled trans-Sahara trade
Kingdom of Benin and Kongo were two famous dynasties
Village and family bonds formed the basis of life
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES OF THE 1400S
European villages had a long tradition of social hierarchy – complete with nobles, merchants & peasants
Christianity played a critical role – religious leaders had power
The Reformation in the early 1500s led to a split in the church
EUROPEAN EXPLORATION
God, Gold, and Glory
Improved map making, better sailboats, compasses, astrolabes, – all led to better exploration
Astroble
AGE OF DISCOVERY
SPANISH NORTH AMERICA – SECTION 2
Columbus crosses the Atlantic in October of 1492 and lands in San Salvador (“Holy Savior”)
He spent about 3 months exploring Islands in the Bahamas
Europeans used advanced weapons to force locals into labor: Plantation System
Disease devastated Native population
Columbus in the Caribbean
IMPACT OF COLUMBUS
On Africans- Before slave trade ended in the 1800s, 10 million Africans
On Europeans- Biggest voluntary migration in world history
 |
| Lines dividing the non-Christian world between Spain and Portugal: the 1494 Tordesillas meridian (purple) and the 1529 Zaragoza antimeridian (green) |
On Trade- Columbian Exchange meant new goods & products flowed between continents
The Columbian Biological Exchange
The letter that launched a thousand ships: Columbus' letter telling of the New World
SPAIN CLAIMS A NEW EMPIRE
 |
| This is the meeting of Cortes and Montezuma, king of the Aztecs. The Aztecs were at their height, strong and still conquering their neighbors when they fell to the Spanish. |
Spanish explorers (Conquistadors) seized much of the Americas
 |
| This is Hernan Cortes. He was the one who conquered and destroyed the Aztec Empire. He once said that he and his men were slaves to gold. |
Cortes conquered the Aztecs in Mexico
 |
| These Tlaxcala soldiers are leading Cortes to the attack on the Aztecs. The Tlaxcala made a treaty with the Spanish that if they helped Cortes they would be left unmolested, receive half the spoils, and never be taxed or forced to pay tribute to the Spanish. The Spanish kept this bargain for 300 years. |
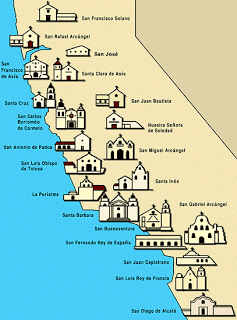
Mid-1500s, Spain explored much of what is today the SW & West of the USA
New Mexico settled by Spanish priest who converted Natives (Pueblos)
Texas area had 30 expeditions in 16th century
California was site of numerous missions
EARLY BRITISH COLONIES – SECTION 3
Beginning in the early 1600s, the English established colonies along the eastern coast of North America
1607: Jamestown was first to be settled
John Smith
 |
Captain John Smith, based on an engraving done in 1616.
John Smith Map of 1616 (colorized by Preservation Virginia).
led this group of settlers
Colony struggled at first, then was saved by Tobacco crop
 |
 |
 |
| Jamestown |
PURITANS CREATE A “NEW ENGLAND”
The 16th century Reformation caused a split in the Christian Church; Catholics and Protestants
One extreme group of Protestant reformers – the Puritans sought to cleanse or “purify” their religion of all traces of Catholicism
King Philip’s War was fought in 1675 between the Natives and Puritans ending a year later with many dead and the Natives retreating
SETTLING THE MIDDLE COLONIES
Dominated by Dutch and Quaker settlers, the Middle Colonies were founded in the mid-1600s
William Penn led Quakers as they colonized Pennsylvania and Delaware
Portrait of Young William Penn in Armor, date and artist unknown.
Wampum belt, legend dated 1682. Lenape Tribe; clam and whelk shell beads, leather.
ENGLAND’S COLONIES PROSPER
 |
| James was a Stuart king of England, Scotland and Ireland who in 1688 was overthrown in the 'Glorious Revolution' by William III. |
 |
| George III was King of Great Britain and Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two countries on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until his death. |
By 1752, the English Crown had assumed more & more responsibility for the 13 colonies
Mercantilism & Navigation Acts were two such ways that the English government controlled the colonies
NAVIGATION ACTS
 |
| Dutch and English Ships |
These laws restricted the colonies shipping & trade
Ships, destinations, crews, goods: All strictly regulated by the English
The colonies were developing a spirit of self-determination. Therefore, they were NOT happy with these restrictions
 | |
| the economic theory that trade generates wealth and is stimulated by the accumulation of profitable balances, which a government should encourage by means of protectionism. |
Mercantilism
THE COLONIES COME OF AGE – SECTION 4
 |
| New England Ship Yard |
 |
| Fleet of Ships for tobacco trade |
New England, Middle Colonies, and the South – all developed distinct economies and societies
In the South, rural Plantations with a single cash crop were common
and African slaves made up the majority of people
Small Southern farmers (Germans, Scots, Irish)
THE MIDDLE PASSAGE
During the 17th century, Africans endured a transatlantic crossing from Africa to the North American Colonies
Cruelty characterized the months long journey – 13% died on route
AFRICANS MAINTAIN PARTS OF THEIR CULTURE
Despite enslavement, Africans coped with the horrors of slavery via music, dance, and storytelling
Slaves also resisted their position of subservience by faking illness, breaking tools, or work slowdowns
Others were more radical and tried escape & revolt
NORTHERN COLONIES COMMERCE THRIVES
The development of cities, expansion of trade, and diverse economies gradually made the North radically different from the South
Philly was the 2nd largest British port
Farming differed from the South: smaller, more diverse crops in North
THE ENLIGHTENMENT AND THE GREAT AWAKENING
1700s: An intellectual movement known as the Enlightenment began in Europe and a religious movement known as the Great Awakening started in the Colonies
The Enlightenment emphasized reason, science, and observation and led to the discovery of natural laws
Enlightenment
John Locke
Great Awakening
Glorious Revolution
All provided a unifying experience that bridged colonial divides of faith, region, and class
Glorious Revolution
James II was overthrown in England
Encouraged colonial uprising against British authority in Massachusetts, New York, and Maryland
Enlightenment
Encouraged people to study the world around them and think for themselves
Ben Franklin created the “American Philosophical Society” to improve society
John Locke
Believed people had natural rights because they were human
People formed governments to protect these rights
If government fails to protect rights people can revolt and create a new government
Influenced many founding fathers, including Thomas Jefferson
Ideas can be found throughout the Declaration of Independence
RELIGIOUS REVIVAL: THE GREAT AWAKENING
A series of religious revivals aimed at restoring devotion & piety swept through the colonies in the mid-1700s
Jonathan Edwards was a Puritan priest from New England who was instrumental in the movement
Fire & Brimstone style of worship; large, emotionally charged crowds
Like the Enlightenment the movement stressed the importance of the individual
Painting by Junius Brutus Stearns, circa 1850. Courtesy Virginia Museum of Fine Arts.
Competition in North America led to a war (1754-1763) between old rivals France and England
The French in North America were tradesmen (furs) not long-term inhabitants
Ohio River valley was the site of the conflict
The Colonists supported the British while the Natives supported the French
The French in North America were tradesmen (furs) not long-term inhabitants
Ohio River valley was the site of the conflict
The Colonists supported the British while the Natives supported the French
BRITAIN DEFEATS AN OLD ENEMY
While the French had early victories, the British led by William Pitt and GeorgeWashington eventually defeated the French
Treaty of Paris ends the war in 1763
Brits claim most of North America including Florida (from French ally Spain) & Canada
Native Americans also realized a French loss was a Native American loss
 |
| William Pitt |
PROCLAMATION LINE OF 1763
e population